(Tco 6) After Connecting to an Ftp Site
This document describes unlike FTP and TFTP inspection scenarios on the Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and it also covers ASA FTP/TFTP inspection configuration and basic troubleshooting.
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you take knowledge of these topics:
-
Basic communication between required interfaces
-
Configuration of the FTP server located in the DMZ network
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
-
ASA 5500 or ASA 5500-Ten Series ASA that runs the 9.ane(v) software image
- Whatever FTP Server
-
Any FTP Client
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environs. All of the devices used in this certificate started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you empathize the potential bear on of any control.
The Security Apparatus supports application inspection through the Adaptive Security Algorithm office. Through the stateful application inspection used by the Adaptive Security Algorithm, the Security Appliance tracks each connection that traverses the firewall and ensures that they are valid. The firewall, through stateful inspection, too monitors the state of the connection to compile information to place in a country tabular array. With the utilise of the land table in addition to ambassador-defined rules, filtering decisions are based on context that is established by packets previously passed through the firewall.
The implementation of awarding inspections consists of these actions:
-
Identify the traffic
-
Apply inspections to the traffic
-
Actuate inspections on an interface
There are two forms of FTP as shown in the image.
-
Active style
-
Passive mode
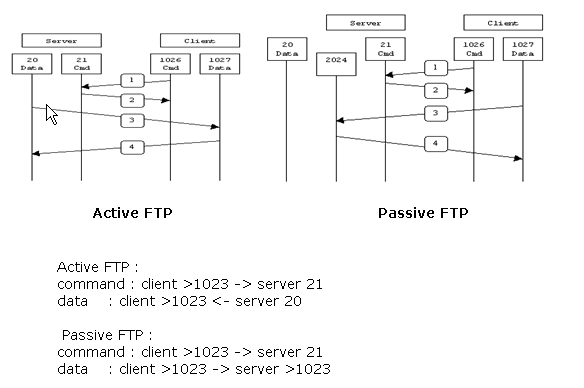
Agile FTP
In Active FTP style, the customer connects from a random unprivileged port (North>1023) to the control port (21) of the FTP server. Then the client starts to heed to port Northward>1023 and sends the FTP command port N>1023 to the FTP server. The server and so connects back to the specified data ports of the client from its local data port, which is port xx.
Passive FTP
In Passive FTP mode, the client initiates both connections to the server, which solves the problem of a firewall that filters the incoming data port connectedness to the customer from the server. When an FTP connection is opened, the client opens two random unprivileged ports locally. The first port contacts the server on port 21. But instead of running a port command and allowing the server to connect dorsum to its information port, the client problems the PASV command. The result of this is that the server then opens a random unprivileged port (P>1023) and sends the port P command back to the client. The customer then initiates the connection from port N>1023 to port P on the server to transfer data. Without the inspection control configuration on the Security Appliance, FTP from inside users headed outbound works only in Passive way. Also, users outside headed entering to your FTP server are denied access.
TFTP
TFTP, as described in RFC 1350, is a simple protocol to read and write files between a TFTP server and customer. TFTP uses UDP port 69.
Avant-garde Protocol Handling
Why practice you demand FTP inspection?
Some applications crave special treatment by the Cisco Security Appliance application inspections part. These types of applications typically embed IP addressing data in the user data packet or open secondary channels on dynamically assigned ports. The application inspection office works with Network Address Translation (NAT) in order to help identify the location of embedded addressing information.
In addition to the identification of embedded addressing information, the awarding inspection function monitors sessions in gild to determine the port numbers for secondary channels. Many protocols open secondary TCP or UDP ports to meliorate functioning. The initial session on a well-known port is used to negotiate dynamically assigned port numbers.
The application inspection office monitors these sessions, identifies the dynamic port assignments and permits data commutation on these ports for the duration of the specific sessions. Multimedia and FTP applications exhibit this kind of behavior.
If the FTP inspection has not been enabled on the Security Apparatus, this asking is discarded and the FTP sessions do non transmit whatever requested information.
If the FTP inspection is enabled on the ASA, then the ASA monitors the control channel and tries to recognize a request to open the data channel. The FTP protocol embeds the data-channel port specifications in the control aqueduct traffic, requiring the Security Appliance to inspect the control channel for data-port changes.
Once the ASA recognizes a request, it temporarily creates an opening for the data-aqueduct traffic that lasts for the life of the session. In this fashion, the FTP inspection part monitors the command channel, identifies a data-port assignment, and allows data to exist exchanged on the information port for the length of the session.
ASA inspects port 21 connections for FTP traffic past default through the global-inspection class-map. The Security Appliance too recognizes the difference between an agile and a passive FTP session.
If the FTP sessions support passive FTP data transfer, the ASA through the inspect ftp command, recognizes the data port request from the user and opens a new data port greater than 1023.
The inspect ftp command inspection inspects FTP sessions and performs iv tasks:
- Prepares a dynamic secondary information connection
- Tracks the FTP command-response sequence
- Generates an audit trail
- Translates the embedded IP address using NAT
FTP application inspection prepares secondary channels for FTP data transfer. The channels are allocated in response to a file upload, a file download, or a directory listing outcome, and they must be pre-negotiated. The port is negotiated through the PORT or PASV (227) commands.
Notation: All the network scenarios are explained with FTP inspection enabled on the ASA.
Scenario 1. FTP Client Configured for Active Fashion
Client connected to Inside Network of the ASA and Server in Exterior Network.
Network Diagram
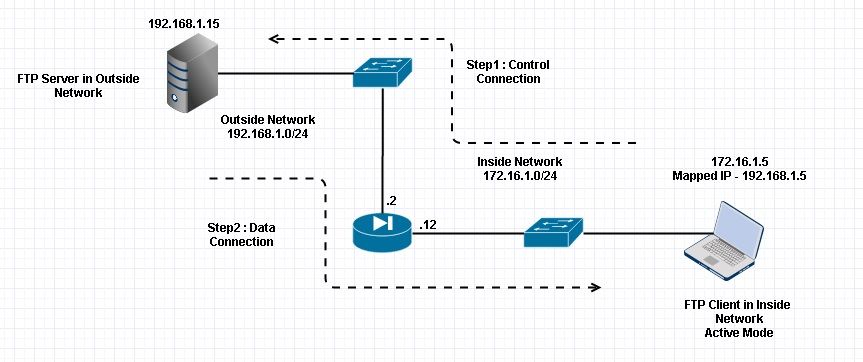
Note: The IP addressing schemes used in this configuration are non legally routable on the Net.
Equally shown in this image, the network setup used has the ASA with Client in the Inside Network with IP 172.16.1.5. Server is in Outside Network with IP 192.168.1.xv. Client has a mapped IP 192.168.ane.5 in the Outside Network .
There is no need to allow any Admission-list on Exterior Interface as FTP inspection opens Dynamic Port Channel.
Configuration Example:
ASA Version 9.one(5) ! hostname ASA domain-name corp.com enable password WwXYvtKrnjXqGbu1 encrypted names ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif Outside
security-level 0
ip address 192.168.i.ii 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif Within
security-level l
ip accost 172.xvi.1.12 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/ii
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip accost
!
interface Management0/0
management-simply
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!--- Output is suppressed. !--- Object groups is created to define the host.
object network obj-172.sixteen.1.5
subnet 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 !--- Object NAT is created to map Within Customer to Outside subnet IP.object network obj-172.xvi.1.five
class-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map blazon inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters message-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy form inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map audit ftp inspect h323 h225 audit h323 ras inspect netbios audit rsh inspect rtsp inspect skinny inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet audit sunrpc inspect tftp inspect sip inspect xdmcp ! !--- This command tells the device to !--- use the "global_policy" policy-map on all interfaces. service-policy global_policy global prompt hostname context Cryptochecksum:4b2f54134e685d11b274ee159e5ed009 : end ASA(config)#
nat (Inside,Outside) dynamic 192.168.1.v
Verify
Connectedness
Customer in Inside Network running Active FTP:Ciscoasa(config)# sh conn
three in employ, iii almost usedTCP Exterior 192.168.1.15:20 inside 172.16.1.5:61855, idle 0:00:00, bytes 145096704, flags UIB <--- Dynamic Connection Opened
TCP Outside 192.168.1.xv:21 within 172.16.1.v:61854, idle 0:00:00, bytes 434, flags UIO
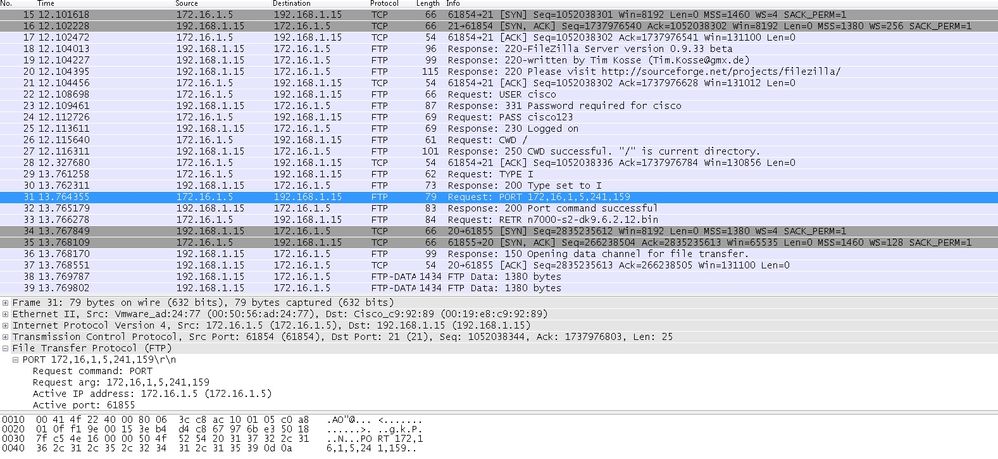
Here the client in Within initiates the connection with source port 61854 to the destination port 21. Client then sends Port command with 6 tuple value. Server in turn initiates the Secondary/Data connection with Source Port of 20 and Destination Port is calculated from the steps mentioned after these captures.
Capture Inside Interface every bit shown in this image.
Capture Exterior Interface as shown in this image.
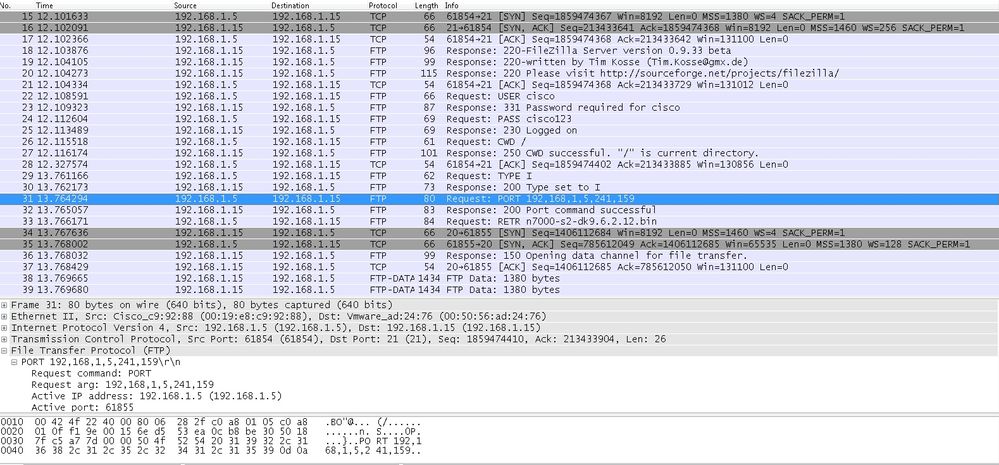
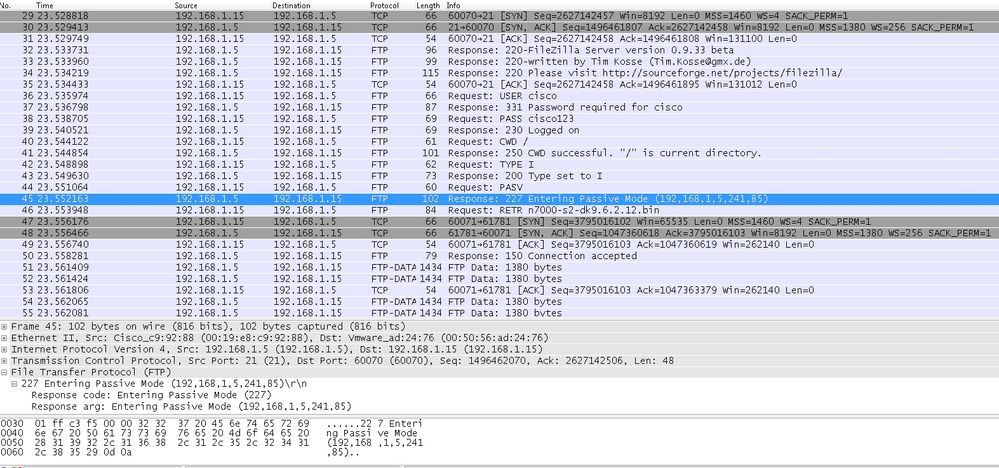
Port Value is calculated using last two touple out of 6. Left 4 tuple are IP accost and 2 touple are for Port. As shown in this image, IP address is 192.168.i.5 and 241*256 + 159 = 61855.
Capture besides shows that the values with Port Commands are changed when FTP inspection is enabled. Within Interface Capture shows the real value of IP and the port sent by Client for Server to connect to Client for Data Channel and Outside Interface Capture shows mapped accost.
Scenario ii. FTP Client Configured for Passive Mode
Client in Within Network of the ASA and Server in Exterior Network.
Network Diagram
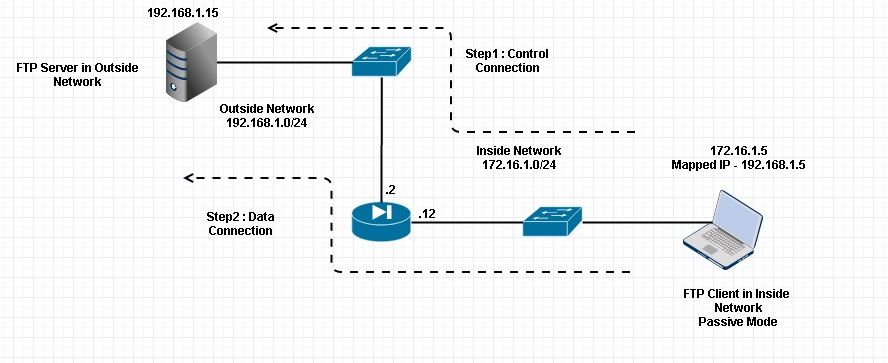
Connection
Customer in Inside Network running Passive Mode FTP:ciscoasa(config)# sh conn
iii in apply, 3 most usedTCP Outside 192 .168.i.15:60142 inside 172.16.1.v:61839, idle 0:00:00, bytes 184844288, flags UI <--- Dynamic Connection Opened.
TCP Exterior 192.168.1.fifteen:21 inside 172.sixteen.one.five:61838, idle 0:00:00, bytes 451, flags UIO
Hither the customer in within initiates a connection with Source Port 61838 the Destination Port of 21. As information technology is a Passive FTP, client initiates both the connections. Therefore, after Client Sends PASV control, server replies with its 6 tuple value and client connects to that Socket for Data connexion.
Capture Inside Interface as shown in this image.
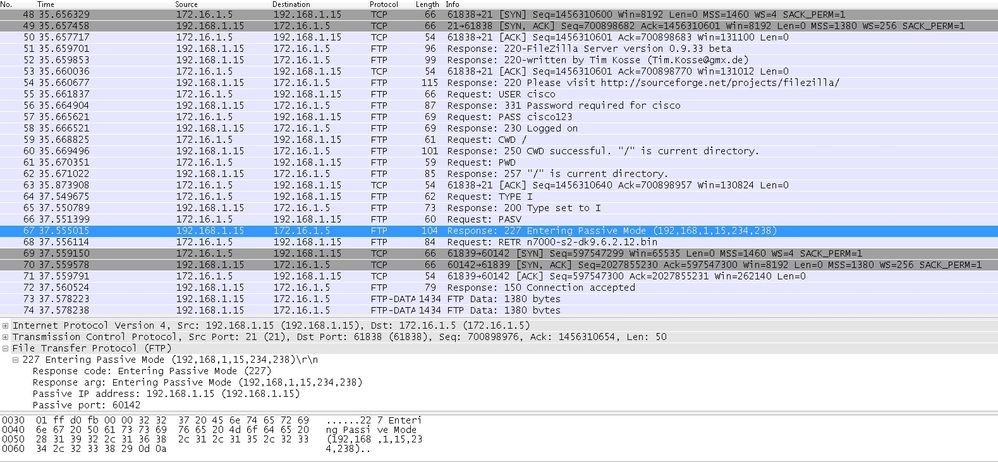
Capture Outside Interface equally shown in this image.
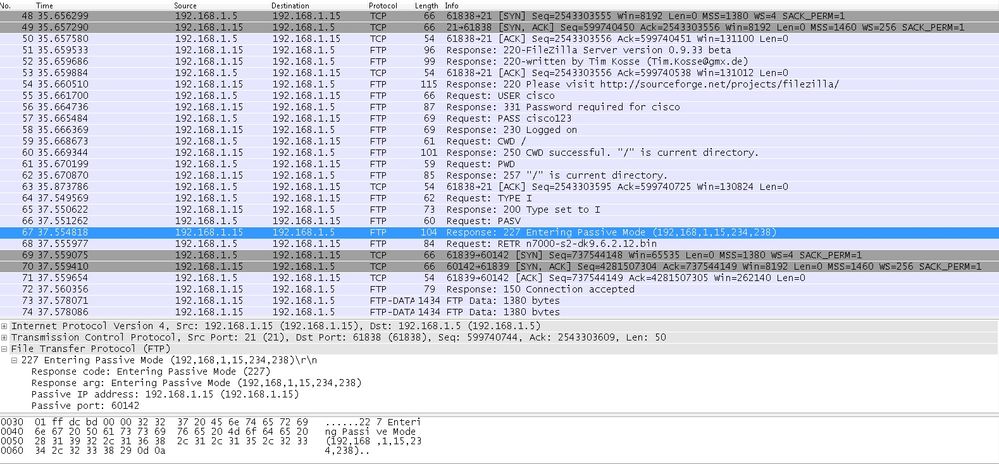
Calculation for the Ports remains the same.
Equally mentioned earlier, the ASA re-writes the embedded IP values if FTP inspection is enabled. Besides, it does open up a dynamic port aqueduct for data connection.
These are the connexion details if FTP Inspection is Disabled
Connectedness:
ciscoasa(config)# sh conn
2 in utilize, 3 most usedTCP Exterior 192.168.1.15:21 inside 172.sixteen.1.v:61878, idle 0:00:09, bytes 433, flags UIO
TCP Outside 192.168.1.15:21 inside 172.16.1.5:61875, idle 0:00:29, bytes 259, flags UIO
Without FTP inspection, It but tries to send port control once again and again but at that place is no reply equally outside receives the PORT with Original IP not NATTed i. Same has been shown in the dump.
FTP inspection can be disabled with no fixup protocol ftp 21 control in configuration terminal mode.
Without FTP inspection, merely PASV control works when customer is in Inside every bit there is there is no port control coming from Inside which needs to be embedded and both the connections are initiated from Inside.
Scenario 3. FTP Client Configured for Active Mode
Client in Outside Network of the ASA and Server in DMZ Network.
Network Diagram
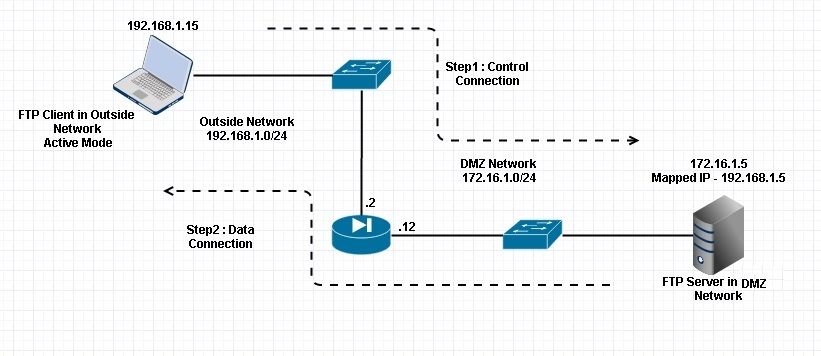
Configuration:
ASA(config)#show running-config ASA Version 9.1(5) ! hostname ASA domain-name corp.com enable password WwXYvtKrnjXqGbu1 encrypted names ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif Outside
security-level 0
ip address 192.168.1.ii 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif DMZ
security-level 50
ip accost 172.xvi.ane.12 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/two
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Management0/0
management-only
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip accost
!--- Output is suppressed.
!--- Permit inbound FTP control traffic.access-listing 100 extended permit tcp any host 192.168.1.v eq ftp
!--- Object groups are created to define the hosts.
object network obj-172.16.1.5
host 172.16.1.5 !--- Object NAT is created to map FTP server with IP of Outside Subnet.object network obj-172.16.1.five
nat (DMZ,Outside) static 192.168.ane.5
access-group 100 in interface outside
form-map inspection_default match default-inspection-traffic ! ! policy-map blazon inspect dns preset_dns_map parameters bulletin-length maximum 512 policy-map global_policy form inspection_default inspect dns preset_dns_map audit ftp inspect h323 h225 inspect h323 ras inspect netbios audit rsh inspect rtsp inspect skinny inspect esmtp inspect sqlnet inspect sunrpc audit tftp inspect sip inspect xdmcp ! !--- This command tells the device to !--- use the "global_policy" policy-map on all interfaces. service-policy global_policy global prompt hostname context Cryptochecksum:4b2f54134e685d11b274ee159e5ed009 : end ASA(config)#
Verify
Connection:
Customer in Outside Network running in Active Mode FTP:ciscoasa(config)# sh conn
3 in use, 3 most usedTCP outside 192.168.1.xv:55836 DMZ 172.16.i.5:21, idle 0:00:00, bytes 470, flags UIOB
TCP outside 192.168.ane.fifteen:55837 DMZ 172.sixteen.ane.5:twenty, idle 0:00:00, bytes 225595694, flags UI <--- Dynamic Port channel
Capture DMZ Interface as shown in this prototype.
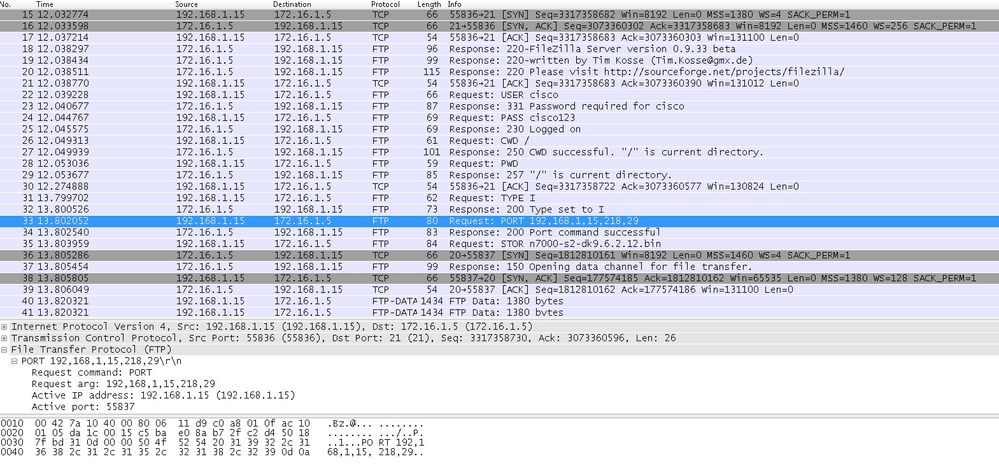
Capture Outside Interface as shown in this image.
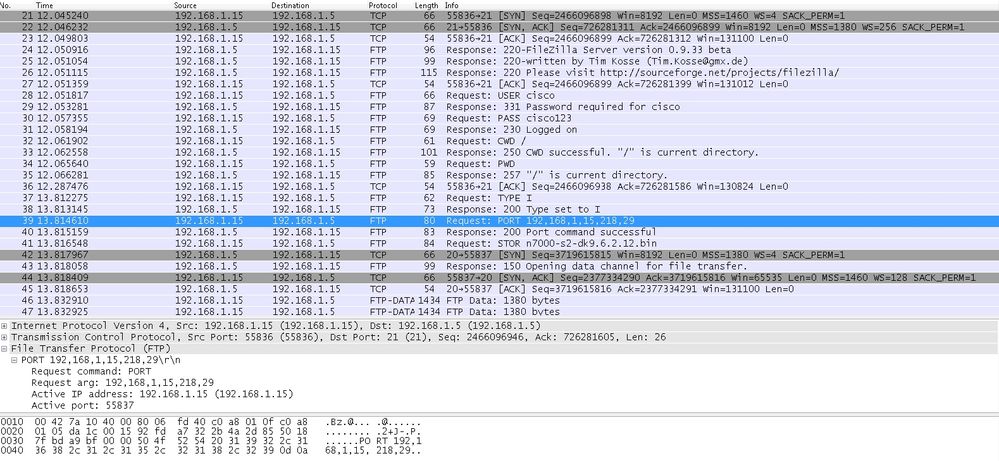
Hither, the client is runs Active Mode Client 192.168.ane.15 and initiates connexion to server in DMZ on port 21. Client and then sends port command with half-dozen tuple value to server to connect to that specific dynamic port. Server so initiates the information connexion with Source Port equally 20.
Scenario 4. FTP Client Running Passive Mode
Customer in Outside Network of the ASA and Server in DMZ Network.
Network Diagram
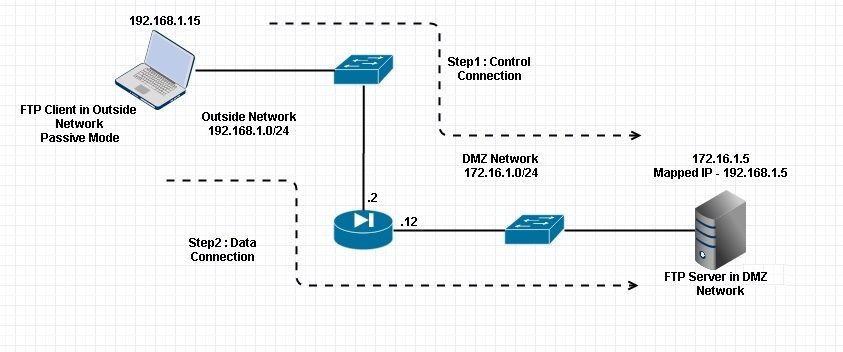
Connection
Client in Exterior Network running in Passive Mode FTP:ciscoasa(config)# sh conn
3 in use, 3 most usedTCP Outside 192.168.i.15:60071 DMZ 172.sixteen.1.5:61781, idle 0:00:00, bytes 184718032, flags UOB <--- Dynamic channel Open
TCP Outside 192.168.ane.15:60070 DMZ 172.sixteen.1.5:21, idle 0:00:00, bytes 413,
flags UIOB
Capture DMZ Interface every bit shown in this image.
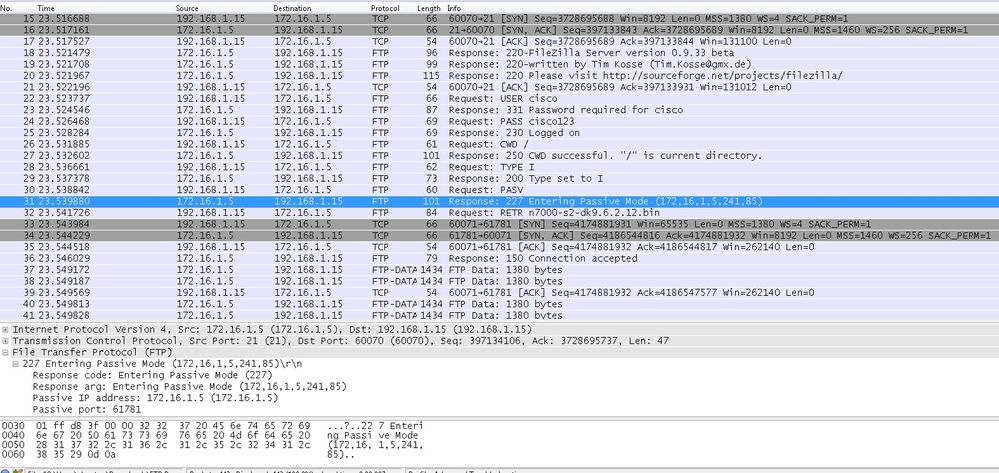
Capture Exterior Interface as shown in this paradigm.
Configure Bones FTP Awarding Inspection
By default, the configuration includes a policy that matches all default application inspection traffic and applies inspection to the traffic on all interfaces (a global policy). Default application inspection traffic includes traffic to the default ports for each protocol.
You lot can simply apply ane global policy, and then if y'all want to alter the global policy, for instance, to apply inspection to non-standard ports, or to add inspections that are not enabled by default, yous need to either edit the default policy or disable it and apply a new one. For a listing of all default ports, refer to the Default Inspection Policy.
-
Run the policy-map global_policy control.
ASA(config)#policy-map global_policy
-
Run the class inspection_default command.
ASA(config-pmap)#class inspection_default
-
Run the inspect FTP command.
ASA(config-pmap-c)#inspect FTP
- There is an selection to use the inspect FTP strict command. This control increases the security of protected networks by preventing a spider web browser from sending embedded commands in FTP requests.
After you lot enable the strict option on an interface, FTP inspection enforces this behavior:
-
An FTP command must be best-selling before the Security Appliance allows a new command
-
The Security Appliance drops a connection that sends embedded commands
-
The 227 and PORT commands are checked to ensure that they do non appear in an error string
Warning: The utilize of the strict option might cause the failure of FTP clients that are not strictly compliant with FTP RFCs. Refer to Using the strict Option for more information on the apply of the strict selection.
-
Configure FTP Protocol Inspection on Non-Standard TCP Port
You lot tin can configure the FTP Protocol Inspection for non-standard TCP ports with these configuration lines (replace XXXX with the new port number):
access-listing ftp-list extended allow tcp any any eq XXXX ! class-map ftp-class match access-list ftp-list ! policy-map global_policy form ftp-course inspect ftp
Verify
In order to ensure that the configuration has successfully taken, run the show service-policy command. Also, limit the output to the FTP inspection by running the show service-policy audit ftp control.
ASA#show service-policy audit ftp Global Policy: Service-policy: global_policy Class-map: inspection_default Inspect: ftp, packet 0, drop 0, reste-driblet 0 ASA#
TFTP inspection is enabled past default.
The security appliance inspects TFTP traffic and dynamically creates connections and translations, if necessary, to let file transfer between a TFTP client and server. Specifically, the inspection engine inspects TFTP Read Requests (RRQ), Write Requests (WRQ), and Error Notifications (ERROR).
A dynamic secondary channel and a PAT translation, if necessary, are allocated on a reception of a valid RRQ or WRQ. This secondary channel is afterward used by TFTP for file transfer or error notification.
Only the TFTP server can initiate traffic over the secondary channel, and at most one incomplete secondary channel can exist between the TFTP client and server. An fault notification from the server closes the secondary channel.
TFTP inspection must be enabled if fstatic PAT is used to redirect TFTP traffic.
Configure Bones TFTP Application Inspection
Past default, the configuration includes a policy that matches all default application inspection traffic and applies inspection to the traffic on all interfaces (a global policy). Default awarding inspection traffic includes traffic to the default ports for each protocol.
You can only apply one global policy. And then if you desire to alter the global policy, for example, to apply inspection to non-standard ports, or to add inspections that are not enabled by default, you need to either edit the default policy or disable information technology and employ a new one. For a list of all default ports, refer to the Default Inspection Policy.
-
Run the policy-map global_policy command.
ASA(config)#policy-map global_policy
-
Run the course inspection_default command.
ASA(config-pmap)#class inspection_default
-
Run the inspect TFTP command.
ASA(config-pmap-c)#inspect TFTP
Network Diagram
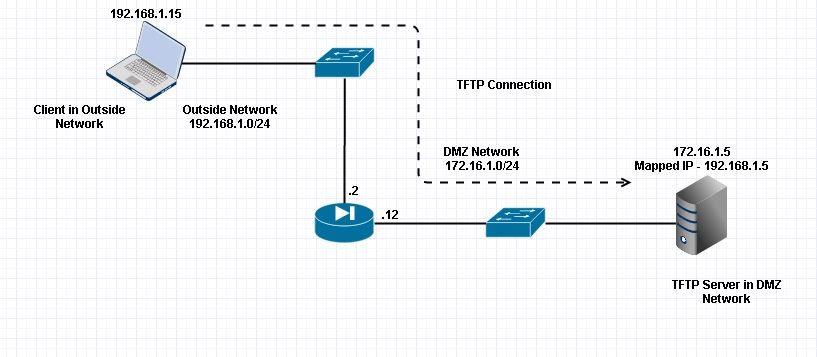
Here the customer in configured in Exterior Network. TFTP server is placed in DMZ Network. Server is mapped to the IP 192.168.ane.5 which is in Exterior Subnet.
Configuration Example:
ASA(config)#show running-config ASA Version ix.one(5) ! hostname ASA domain-name corp.com enable countersign WwXYvtKrnjXqGbu1 encrypted names ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif Outside
security-level 0
ip accost 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/i
nameif DMZ
security-level fifty
ip address 172.sixteen.ane.12 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
shutdown
no nameif
security-level 100
ip address ten.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Management0/0
direction-only
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!--- Output is suppressed. !--- Permit entering TFTP traffic. access-listing 100 extended permit udp whatsoever host 192.168.i.five eq tftp ! !--- Object groups are created to ascertain the hosts. object network obj-172.16.1.5
host 172.16.one.5 !--- Object NAT to map TFTP server to IP in Outside Subnet.
object network obj-172.sixteen.ane.5
nat (DMZ,Exterior) static 192.168.i.vadmission-grouping 100 in interface outside
course-map inspection_defaultmatch default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
bulletin-length maximum 512policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
audit h323 ras
audit netbios
inspect rsh
audit rtsp
inspect skinny
inspect esmtp
audit sqlnet
inspect sunrpc
inspect tftp
inspect sip
inspect xdmcp
!!--- This command tells the device to
!--- use the "global_policy" policy-map on all interfaces.service-policy global_policy global
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:4b2f54134e685d11b274ee159e5ed009
: terminate
ASA(config)#
Verify
In club to ensure the configuration has successfully taken, run the show service-policy command. Also, limit the output to the TFTP inspection only by running the bear witness service-policy audit tftp command.
ASA#bear witness service-policy inspect tftp Global Policy: Service-policy: global_policy Form-map: inspection_default Inspect: tftp, packet 0, drop 0, reste-drop 0 ASA#
This department provides information you lot tin apply in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
Parcel Tracer
Client in Inside Network
FTP customer Inside - Packet Tracer for Control Connectedness : Same Flow for Active and Passive.# packet-tracer input within tcp 172.16.1.5 12345 192.168.1.15 21 det
-----Omitted------
Stage: 5
Type: Audit
Subtype: inspect-ftp
Result: Let
Config:
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
policy-map global_policy
form inspection_default
inspect ftp
service-policy global_policy global
Boosted Data:
Forward Menses based lookup yields rule:
in id=0x76d9a120, priority=lxx, domain=inspect-ftp, deny=false
hits=2, user_data=0x76d99a30, cs_id=0x0, use_real_addr, flags=0x0, protocol=6
src ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=0
dst ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=21, dscp=0x0
input_ifc=inside, output_ifc=whatsoeverPhase: 6
Type: NAT
Subtype:
Result: Permit
Config:
object network obj-172.sixteen.1.5
nat (inside,outside) static 192.168.1.5
Additional Information:
NAT divert to egress interface DMZ
interpret 172.xvi.1.v/21 to 192.168.ane.v/21Stage: vii
Type: NAT
Subtype: rpf-bank check
Result: Allow
Config:
object network obj-172.16.1.v
nat (inside,outside) static 192.168.1.5
Additional Data:
Forward Catamenia based lookup yields rule:
out id=0x76d6e308, priority=6, domain=nat-reverse, deny=faux
hits=xv, user_data=0x76d9ef70, cs_id=0x0, use_real_addr, flags=0x0, protocol=0
src ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=0
dst ip/id=172.sixteen.1.five, mask=255.255.255.255, port=0, dscp=0x0
input_ifc=inside, output_ifc=outside----Omitted----
Upshot:
input-interface: inside
input-status: up
input-line-status: upward
output-interface: Outside
output-status: up
output-line-status: up
Action: allow
Client in Exterior Network
FTP client Outside - Packet Tracer for Control Connectedness : Aforementioned Flow for Active and Passive# packet-tracer input outside tcp 192.168.1.15 12345 192.168.one.five 21 det
Stage: i
Type: UN-NAT
Subtype: static
Outcome: Let
Config:
object network obj-172.16.1.five
nat (DMZ,exterior) static 192.168.1.5
Additional Information:
NAT divert to egress interface DMZ
Untranslate 192.168.ane.5/21 to 172.16.1.v/21-----Omitted-----
Phase: 4
Blazon: INSPECT
Subtype: audit-ftp
Consequence: ALLOW
Config:
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
audit ftp
service-policy global_policy global
Additional Information:
Forward Menstruum based lookup yields rule:
in id=0x76d84700, priority=seventy, domain=inspect-ftp, deny=false
hits=17, user_data=0x76d84550, cs_id=0x0, use_real_addr, flags=0x0, protocol=half-dozen
src ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=0
dst ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=21, dscp=0x0
input_ifc=outside, output_ifc=anyStage: v
Type: NAT
Subtype: rpf-check
Result: Permit
Config:
object network obj-172.xvi.1.5
nat (DMZ,outside) static 192.168.i.v
Boosted Information:
Forward Menstruation based lookup yields dominion:
out id=0x76d6e308, priority=six, domain=nat-reverse, deny=simulated
hits=17, user_data=0x76d9ef70, cs_id=0x0, use_real_addr, flags=0x0, protocol=0
src ip/id=0.0.0.0, mask=0.0.0.0, port=0
dst ip/id=172.16.1.v, mask=255.255.255.255, port=0, dscp=0x0
input_ifc=outside, output_ifc=DMZ----Omitted-----
Result:
input-interface: Outside
input-status: up
input-line-condition: upward
output-interface: DMZ
output-condition: up
output-line-condition: up
Activity: allow
Equally seen in both the package-tracers, the traffic hits their respective NAT statements and FTP inspection Policy. They also go out their required interfaces.
During troubleshooting, you lot can endeavour to capture the ASA Ingress and Egress interfaces and see if the ASA Embedded IP address re-write is working fine and cheque the connection if the dynamic port is being allowed on ASA.
Source: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/content-networking/file-transfer-protocol-ftp/200194-ASA-9-x-Configure-FTP-TFTP-Services.html
0 Response to "(Tco 6) After Connecting to an Ftp Site"
Post a Comment